该文章来自于2016年后半年整理的算法源码笔记,由于之前没有写博客的习惯,都直接以笔记的形式存在电脑上,分享起来非常不便,因此抽出时间,将其整理成博客的形式,和大家一起学习交流。
决策树算法简要介绍
决策树算法是一种常见的分类算法,也可以用于回归问题。相对于其他分类算法,决策树的优点在于简单,可解释性强;对特征尺度不敏感,不需要做太多的特征预处理工作;能够自动挖掘特征之间的关联关系。缺点是比较容易过拟合(通过随机森林可以避免过拟合)
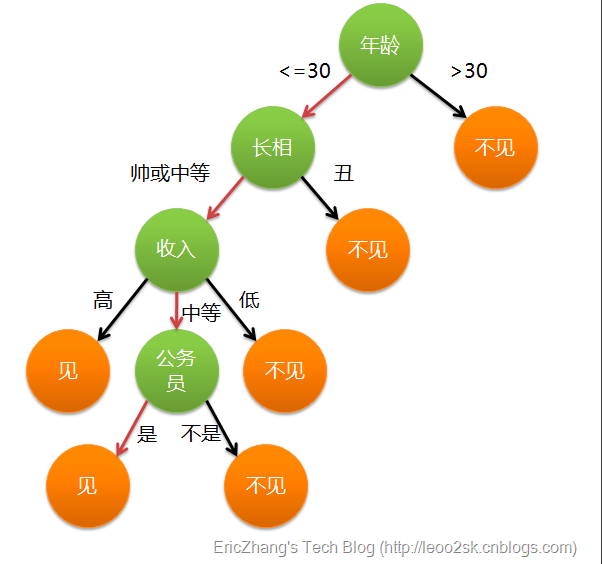
决策树是一个树形结构,其中叶子节点表示分类(或回归)结果,非叶子节点是属性判断判断节点,每个属性判断节点都选择样本的一个特征,并根据该特征的取值决定选择哪一个分支路径。在对样本进行预测时,从根节点开始直到叶子节点,对于路径上的每个分支节点,都根据其对应的属性取值选择下一个分支节点,直到叶子节点。整个完整的路径,表示对样本的预测过程。如图1所示,表示一个女孩在决定是否决定去相亲的一个过程,最终选择去或者不去,对应分类的结果,中间的各种条件对应相关的属性。
决策树的训练
从根节点开始,根据信息增益或其他条件,不断选择分裂的属性,直到生成叶子节点的过程。具体过程如下所示:
- 对不同的属性,计算其信息增益,选择增益最大的特征对应根节点的最佳分裂。
- 从根节点开始,对于不同的分支节点,分别选择信息增益最大的特征作为分支节点的最佳分裂。
- 如果达到停止分裂的条件,则将该节点作为叶子节点:当前节点对应的样本都是一类样本,分类结果为对应的样本的类别;总样本数量小于一定值,或者树的高度达到最大值,或者信息增益小于一定值,或者已经用完所有的属性,选择占比最大的样本分类作为节点对应的分类结果。否则,根据步骤2进一步构造分裂节点。
属性度量
决策树构建的关键,在于不断地选择最佳分裂属性。属性的收益度量方法,常见的有信息增益(ID3算法)、信息增益率(C4.5算法),基尼系数(CART算法)等。
ID3算法:
熵:信息论中,用于描述信息的不确定性,定义如式1,其中$D$表示对样本的一个划分,$m$表示划分的类别数量,$p_i$表示第i个类别的样本数量比例。
$info(D)=-\sum_{i=1}^m p_ilog_2(p_i)\;\;\;(式1)$
假设按照属性A对样本D进行划分,$v$为属性$A$的划分数量。则$A$对$D$划分的期望熵如式2:
$info_A(D)=\sum_{j=1}^v\frac{|D_j|}{|D|}info(D_j)\;\;\;(式2)$
信心增益为上述原始熵和属性A对D划分后期望熵的差值,可以看做是加入信息A后,不确定性的减少程度。信息增益的定义如式3所示:
$gain(A)=info(D)-info_A(D)\;\;\;(式3)$
ID3算法即在每次选择最佳分裂的属性时,根据信息增益进行选择。
C4.5算法:
ID3算法容易使得选取值较多的属性。一种极端的情况是,对于ID类特征有很多的无意义的值的划分,ID3会选择该属性其作为最佳划分。C4.5算法通过采用信息增益率作为衡量特征有效性的指标,可以克服这个问题。
首先定义分裂信息:
$splitInfo_A(D)=-\sum_{j=1}^v\frac{|D_j|}{|D|}log_2(\frac{|D_j|}{|D|})\;\;\;(式4)$
信息增益率:
$gainRatio(A)=\frac{gain(A)}{splitInfo_A(D)}\;\;\;(式5)$
CART算法:
使用基尼系数作为不纯度的度量。
基尼系数:表示在样本集合中一个随机选中的样本被分错的概率,Gini指数越小表示集合中被选中的样本被分错的概率越小,也就是说集合的纯度越高,反之,集合越不纯。当所有样本属于一个类别时,基尼系数最小为0。所有类别以等概率出现时,基尼系数最大。
$GINI(P)=\sum_{k=1}^Kp_k(1-p_k)=1-\sum_{k=1}^K p_k^2\;\;\;(式6)$
由于cart建立的树是个二叉树,所以K的取值为2。对于特征取值超过2的情况,以每个取值作为划分点,计算该划分下对应的基尼系数的期望。期望值最小的划分点,作为最佳分裂使用的特征划分。
spark 决策树源码分析
为加深对ALS算法的理解,该部分主要分析spark mllib中决策树源码的实现。主要包括模型训练、模型预测2个部分
模型训练
决策树伴生类
DecisionTree伴随类,外部调用决策树模型进行训练的入口。通过外部传入数据和配置参数,调用DecisionTree中的run方法进行模型训练, 最终返回DecisionTreeModel类型对象。
1 | object DecisionTree extends Serializable with Logging { |
决策树类
接受strategy参数初始化,并通过对run方法调用随机森林的run方法,通过设置特征集合为全集、树的个数为1,将随机森林训练后结果集中的第一棵树作为结果返回。
1 | class DecisionTree private[spark] (private val strategy: Strategy, private val seed: Int) |
RandomForest私有类run方法,通过run方法完成模型的训练
分布式训练思想:
- 分布式存储样本
- 对于每次迭代,算法都会对一个node集合进行分裂。对于每个node,相关worker计算的的所有相关统计特征全部传递到某个worker进行汇总,并选择最好的特征分裂
- findSplitsBins方法可用于将连续特征离散化,在初始化阶段完成
- 迭代算法
每次都作用于树的边缘节点,如果是随机森林,则选择所有的树的边缘节点。具体迭代步骤如下:- Master 节点: 从node queue中选取节点,如果训练的是随机森林,且featureSubsetStrategy取值不是all,则对于每个节点选择随机特征子集。selectNodesToSplit用于选择待分裂的节点。
- Worer节点: findBestSplits函数,对每个(tree, node, feature, split),遍历所有本地所有样本计算相关特征,计算结果通过reduceByKey传递给某个节点,由该节点汇总数据,得到(feature, split)或者判断是否停止分裂
- Master节点: 收集所有节点分裂信息,更新model, 并将新的model传递给各个worker节点
####1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156def run(
input: RDD[LabeledPoint],
strategy: OldStrategy,
numTrees: Int,
featureSubsetStrategy: String,
seed: Long,
instr: Option[Instrumentation[_]],
parentUID: Option[String] = None): Array[DecisionTreeModel] = {
val timer = new TimeTracker()
timer.start("total")
timer.start("init")
val retaggedInput = input.retag(classOf[LabeledPoint])
//构建元数据
val metadata =
DecisionTreeMetadata.buildMetadata(retaggedInput, strategy, numTrees, featureSubsetStrategy)
instr match {
case Some(instrumentation) =>
instrumentation.logNumFeatures(metadata.numFeatures)
instrumentation.logNumClasses(metadata.numClasses)
case None =>
logInfo("numFeatures: " + metadata.numFeatures)
logInfo("numClasses: " + metadata.numClasses)
}
//每个特征对应的splits和bins
timer.start("findSplits")
val splits = findSplits(retaggedInput, metadata, seed)
timer.stop("findSplits")
logDebug("numBins: feature: number of bins")
logDebug(Range(0, metadata.numFeatures).map { featureIndex =>
s"\t$featureIndex\t${metadata.numBins(featureIndex)}"
}.mkString("\n"))
// Bin feature values (TreePoint representation).
// Cache input RDD for speedup during multiple passes.
//输入
val treeInput = TreePoint.convertToTreeRDD(retaggedInput, splits, metadata)
val withReplacement = numTrees > 1
val baggedInput = BaggedPoint
.convertToBaggedRDD(treeInput, strategy.subsamplingRate, numTrees, withReplacement, seed)
.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK)
// depth of the decision tree
val maxDepth = strategy.maxDepth
require(maxDepth <= 30,
s"DecisionTree currently only supports maxDepth <= 30, but was given maxDepth = $maxDepth.")
// Max memory usage for aggregates
// TODO: Calculate memory usage more precisely.
val maxMemoryUsage: Long = strategy.maxMemoryInMB * 1024L * 1024L
logDebug("max memory usage for aggregates = " + maxMemoryUsage + " bytes.")
/*
* The main idea here is to perform group-wise training of the decision tree nodes thus
* reducing the passes over the data from (# nodes) to (# nodes / maxNumberOfNodesPerGroup).
* Each data sample is handled by a particular node (or it reaches a leaf and is not used
* in lower levels).
*/
// Create an RDD of node Id cache.
// At first, all the rows belong to the root nodes (node Id == 1).
val nodeIdCache = if (strategy.useNodeIdCache) {
Some(NodeIdCache.init(
data = baggedInput,
numTrees = numTrees,
checkpointInterval = strategy.checkpointInterval,
initVal = 1))
} else {
None
}
/*
Stack of nodes to train: (treeIndex, node)
The reason this is a stack is that we train many trees at once, but we want to focus on
completing trees, rather than training all simultaneously. If we are splitting nodes from
1 tree, then the new nodes to split will be put at the top of this stack, so we will continue
training the same tree in the next iteration. This focus allows us to send fewer trees to
workers on each iteration; see topNodesForGroup below.
*/
val nodeStack = new mutable.Stack[(Int, LearningNode)]
val rng = new Random()
rng.setSeed(seed)
// Allocate and queue root nodes.
val topNodes = Array.fill[LearningNode](numTrees)(LearningNode.emptyNode(nodeIndex = 1))
Range(0, numTrees).foreach(treeIndex => nodeStack.push((treeIndex, topNodes(treeIndex))))
timer.stop("init")
while (nodeStack.nonEmpty) {
// Collect some nodes to split, and choose features for each node (if subsampling).
// Each group of nodes may come from one or multiple trees, and at multiple levels.
val (nodesForGroup, treeToNodeToIndexInfo) =
RandomForest.selectNodesToSplit(nodeStack, maxMemoryUsage, metadata, rng)
// Sanity check (should never occur):
assert(nodesForGroup.nonEmpty,
s"RandomForest selected empty nodesForGroup. Error for unknown reason.")
// Only send trees to worker if they contain nodes being split this iteration.
val topNodesForGroup: Map[Int, LearningNode] =
nodesForGroup.keys.map(treeIdx => treeIdx -> topNodes(treeIdx)).toMap
// Choose node splits, and enqueue new nodes as needed.
timer.start("findBestSplits")
RandomForest.findBestSplits(baggedInput, metadata, topNodesForGroup, nodesForGroup,
treeToNodeToIndexInfo, splits, nodeStack, timer, nodeIdCache)
timer.stop("findBestSplits")
}
baggedInput.unpersist()
timer.stop("total")
logInfo("Internal timing for DecisionTree:")
logInfo(s"$timer")
// Delete any remaining checkpoints used for node Id cache.
if (nodeIdCache.nonEmpty) {
try {
nodeIdCache.get.deleteAllCheckpoints()
} catch {
case e: IOException =>
logWarning(s"delete all checkpoints failed. Error reason: ${e.getMessage}")
}
}
val numFeatures = metadata.numFeatures
parentUID match {
case Some(uid) =>
if (strategy.algo == OldAlgo.Classification) {
topNodes.map { rootNode =>
new DecisionTreeClassificationModel(uid, rootNode.toNode, numFeatures,
strategy.getNumClasses)
}
} else {
topNodes.map { rootNode =>
new DecisionTreeRegressionModel(uid, rootNode.toNode, numFeatures)
}
}
case None =>
if (strategy.algo == OldAlgo.Classification) {
topNodes.map { rootNode =>
new DecisionTreeClassificationModel(rootNode.toNode, numFeatures,
strategy.getNumClasses)
}
} else {
topNodes.map(rootNode => new DecisionTreeRegressionModel(rootNode.toNode, numFeatures))
}
}
}
buildMetadata
决策树训练的元数据构造。主要用于计算每个特征的bin数量,以及无序类特征集合, 每个节点使用的特征数量等。其中决策树一般使用所有特征、随机森林分类采用$sqrt(n)$个特征,随机森林回归采用$\frac{n}{3}$个特征
1 | def buildMetadata( |
DecisionTreeMetadata类
1 | private[spark] class DecisionTreeMetadata( |
findSplits
通过使用采样的样本,寻找样本的划分splits和划分后的bins。
划分的思想:对连续特征和离散特征,分别采用不同处理方式。对于每个连续特征,numBins - 1个splits, 代表每个树的节点的所有可能的二值化分;对于每个离散特征,无序离散特征(用于多分类的维度较大的feature)基于特征的子集进行划分。有序类特征(用于回归、二分类、多分类的维度较小的feature)的每个取值对应一个bin.
1 | protected[tree] def findSplits( |
1 | //对每个特征,通过排序的方式,寻找最佳的splits点 |
1 | //将input这个数对应的二进制位置为1的位置加入到当前划分 |
1 | //对于连续特征,找到其对应的splits分割点 |
TreePoint.convertToTreeRDD
调用TreePoint类的convertToTreeRDD方法,RDD[LabeledPoint]转化为RDD[TreePoint]。
1 | def convertToTreeRDD( |
1 | //将单个样本的原始特征,转化为对应的bin特征值,用于训练 |
1 | private def findBin( |
1 | //LabeledPoint类 |
1 | //TreePoint类 |
BaggedPoint.convertToBaggedRDD
RDD[Datum]数据集转换成RDD[BaggedPoint[Datum]的表示类型,
1 | def convertToBaggedRDD[Datum] ( |
1 | //有放回采样,数据转换为RDD[BaggedPoint[Datum]] |
1 | //BaggedPoint类,datum表示数据实例,subsampleWeights表示当前实例在每个采样中的权重。 |
1 | //原始数据(不采样)直接转换为BaggedPoint结构表示 |
1 | //无放回采样,数据转换为RDD[BaggedPoint[Datum]] |
RandomForest.selectNodesToSplit
选择当前迭代待分裂的节点,以及确定每个节点使用的特征。每次选择都根据内存限制、每个节点占用的内存(如果每个节点使用的是采样后的特征),自适应地确定节点个数。
1 | private[tree] def selectNodesToSplit( |
1 | //无放回采样 |
1 | //通过所有特征的对应的bin数量之和,以及同模型类别(分类还是回归),lable数量之间的关系确定当前节点需要使用的字节数 |
RandomForest.findBestSplits
给定selectNodesToSplit方法选择的一组节点,找到每个节点对应的最佳分类特征的分裂位置。求解的主要思想如下:
基于节点的分组进行并行训练:对一组的节点同时进行每个bin的统计和计算,减少不必要的数据传输成本。这样每次迭代需要更多的计算和存储成本,但是可以大大减少迭代的次数
基于bin的最佳分割点计算:基于bin的计算来寻找最佳分割点,计算的思想不是依次对每个样本计算其对每个孩子节点的增益贡献,而是先将所有样本的每个特征映射到对应的bin,通过聚合每个bin的数据,进一步计算对应每个特征每个分割的增益。
对每个partition进行聚合:由于提取知道了每个特征对应的split个数,因此可以用一个数组存储所有的bin的聚合信息,通过使用RDD的聚合方法,大大减少通讯开销。
1 | private[tree] def findBestSplits( |
1 | //得到当前数据点对应的node index输出,模仿对数据的预测过程,从根节点开始向下传播, |
1 | //对于排序类特征,根据数据点、权重,更新每个特征的每个bin信息 |
1 | //相对于orderedBinSeqOp函数,mixedBinSeqOp函数在同时包括排序和非排序特征情况下,更新聚合信息. |
1 | //寻找最佳分裂特征和分裂位置 |
1 | 根据分裂对应的左孩子聚合信息,右孩子聚合信息,计算当前节点不纯度度量的相关统计信息 |
模型预测
通过模型训练生成决策树(随机森林)模型RandomForestModel,随机森林模型继承了树的组合模型TreeEnsembleModel,进一步通过predictBySumming函数,对传进的样本点进行预测。
1 | //对样本点features进行预测 |
1 | //DecisionTreeModel.predict方法 |
1 | //Node. predict方法 |
参考资料
【1】http://spark.apache.org/mllib/
【2】http://www.cnblogs.com/leoo2sk/archive/2010/09/19/decision-tree.html